The concept of a “typical influence area” emerges as a pivotal step in the territory mapping process for franchise brands.
Understanding and defining this area is a foundational element in the blueprint of any franchise, whether mobile or fixed, as it significantly influences strategic decisions and the potential for sustainable growth.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the nuances of defining and utilizing the typical influence area for franchise success, for both mobile and fixed businesses.
Let’s go!
Decoding the typical influence area
The ‘typical influence area’ of a franchise refers to the specific geographic zone from which the majority of its customers are drawn, effectively marking the limits of its market reach and impact.
In franchise business planning, understanding this area is crucial as it informs key decisions about:
- where to locate new franchises,
- how to size your territories
- assess the market potentiel
- how to allocate marketing efforts,
- and the way to tailor products or services to meet local demands.
Accurately defined, this area helps
- ensure efficient resource utilization,
- avoid market saturation,
- and achieve optimal customer engagement,
ultimately contributing to the overall success and growth of the franchise.
But before starting to determine your real influence area, let’s begin by understanding a couple of things.
The key role of travel and drive-time areas
In defining a franchise’s influence area, the concept of isochrones plays a central role. These contours, representing areas of equal travel time, a more accurate representation of a franchise’s reach than traditional radius mapping, as they take into account real-world factors like rivers, mountains or highways.
Travel-time areas offer a dynamic view of a franchise’s reach, highlighting how accessible it is to potential customers.
On the other hand, distance areas is invaluable for mobile businesses, where travel costs and time are directly linked to distance.
Fixed vs. mobile franchises: tailoring your influence area strategy
The application of the influence area varies significantly between fixed and mobile businesses.
For fixed location franchises, such as a retail store or a restaurant, the typical influence area is often a reflection of how far customers are willing to travel to reach the location.
On the other hand, for mobile businesses, like a home services franchise, the influence area centers around how far the business is willing or able to travel to provide its services. Here, the focus shifts to optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness while maintaining high service standards.
Fixed location businesses: define your catchment area
Follow our step-by-step guide to calculate the catchment area using customer data.
Determining the catchment area: your step-by-step guide
Gather your customer data
Compile customer data from various sources like sales transactions, loyalty programs, customer surveys, or online orders. Focus on collecting geographical data, such as customer addresses or zip codes.
Map your data
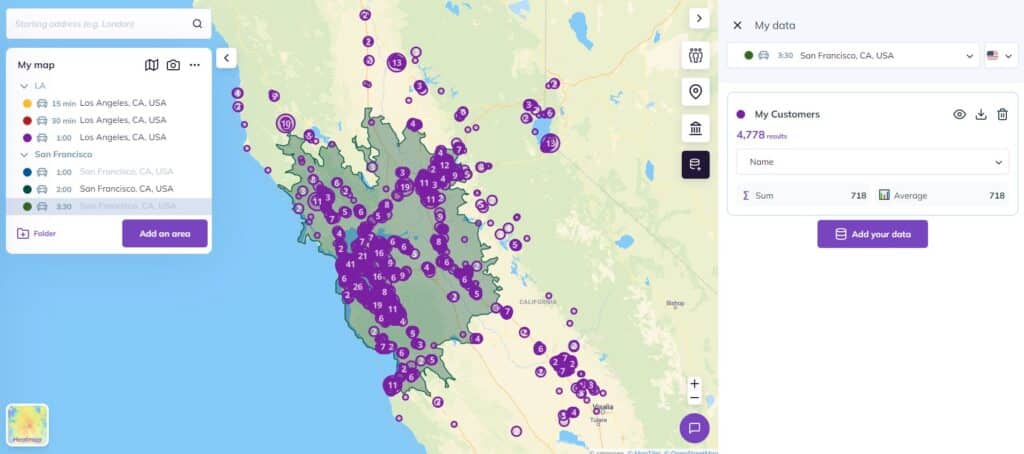
Use a mapping software like Smappen to plot the geographic coordinates of your customers on a map.
>> Tutorial: Importing your own data into the mapVisualize your data on the map
This visual representation will help identify where your customers are concentrated. Then, create a travel-time area from your franchise location that encompasses approximately 80% of your customers.
Alternative methods without customer data
To compensate for a lack of customer data, proactively conduct surveys at your sales locations to gain insights into your customers’ travel habits.
Investigate the duration of their journey to your store and the modes of transportation they use, whether it be walking, driving, or utilizing public transit.
This approach can effectively compensate for the absence of existing customer data, providing valuable information on customer mobility.
Then, use these results by using the same previous step-by-step guide to determine your typical influence area.
Example: Bean There Café

- Brand: Bean There Café
- Industry: Specialty Coffee Shops
- Locations: Urban and suburban areas
Bean There Café wants to define its typical influence area to optimize its existing locations and plan for future expansion. The brand currently operates 30 coffee shops across several cities.
Process:
- Data Collection:
- Customer Surveys: Bean There Café conducts surveys in its top-performing locations, asking customers about their travel time and mode of transportation to the café.
- Sales Data Analysis: The café examines sales data to identify high-traffic times and customer demographics.
- Mapping Customer Addresses:
- Using customer loyalty program data, Bean There Café maps the home or work addresses of frequent customers to visualize where their core customer base is located.
- Defining the Catchment Area:
- Drive Time Analysis: The analysis reveals that 80% of customers come from within a 15-minute drive of each location.
- Public Transport Accessibility: In urban areas, they notice a high concentration of customers living near public transport routes.
- Assessment and Strategy:
- Urban Locations: In city centers, Bean There Café finds its influence area is densely populated but smaller due to higher accessibility and competition. They decide a 10-minute walking radius is optimal.
- Suburban Locations: In suburban areas, the 15-minute drive time radius is more appropriate due to customers relying more on cars.
Mobile businesses: define your service area
Defining the service area for a mobile business involves several strategic steps, each tailored to ensure that the area you serve is both manageable and profitable. Here’s a guide to help you define your service area:
Defining service area: your step-by-step guide
Evaluate business characteristics
Assess the nature of the services offered and their delivery requirements (time, equipment, personnel). Note any unique features of different locations that may affect service delivery (e.g., urban vs. rural settings).
Determine operational capacity
Evaluate the resources (vehicles, staff) available. Calculate average service times, including travel and on-site work.
Define maximum distance and costs
Establish a maximum reasonable travel time or distance for each location, taking into account factors like gasoline costs.
Example: Pet Pals Mobile Grooming

- Brand: Pet Pals Mobile Grooming
- Industry: Pet Grooming Services
- Model: Mobile grooming vans that offer services directly at the customers’ homes
Pet Pals Mobile Grooming is seeking to define its typical service area to improve efficiency and plan for expansion. The company operates a fleet of 20 mobile grooming vans in a metropolitan area and its suburbs.
Process:
- Operational Data Analysis:
- Travel Logs: Pet Pals reviews logs from their vans to understand travel distances and times for appointments.
- Customer Feedback: They gather feedback on how far customers are willing to have the van travel to offer services.
- Defining the Service Area:
- Travel Time and Distance: Analysis shows that most customers are within a 30-minute drive from the van’s home base.
- Cost Analysis: They calculate the cost of travel (fuel, time, vehicle wear) and find that servicing beyond 30 minutes reduces profitability.
- Service Area Strategy:
- Urban and Suburban Differences: In the city, a tighter radius of 20 minutes is set due to traffic congestion. In the suburbs, a 30-minute radius is more feasible and profitable.
- Zoning for Vans: Each van is assigned a specific zone within the metropolitan area, ensuring coverage without overlap.
Whether you are managing a fixed location or a mobile business, a well-defined influence area is the cornerstone of your franchise’s strategic planning. It guides where to establish new locations, how to allocate marketing resources, and tailors your offerings to local demands, all contributing to the overarching goal of franchise success and expansion.
🔍 Focus
Market Penetration:
This refers to the degree to which a franchise brand has established itself in a particular market within its typical influence area. It’s a measure of the brand’s customer base relative to the total potential market in that area.
For a franchise, achieving optimal market penetration means effectively reaching and serving the highest possible percentage of customers within its influence area. It involves not just attracting a large number of customers but also ensuring repeat business and a strong brand presence.
The goal is to dominate the market in the influence area before competitors do, thereby maximizing revenue potential.
The typical influence area defines the boundaries within which these efforts are concentrated.
Operating Costs:
These are the expenses associated with running the franchise on a day-to-day basis.
For fixed location businesses, operating costs include rent, utilities, staff salaries, and inventory. For mobile businesses, costs extend to vehicle maintenance, fuel, and travel time. The typical influence area directly impacts these costs. For instance, servicing a larger area increases travel costs and time, affecting profitability.

